Upgrade Your HPLC System with Silanized Vials from Zhejiang Aijiren Inc.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an analytical technique widely utilized by pharmaceutical, chemical, and biotech industries for separating, identifying, and quantifying components present in mixtures. A critical element of HPLC analysis is the vial that houses your sample to be examined; silanized vials provide more precise results and accurate analyses – in this article, we will highlight their importance.
HPLC analysis relies on a number of components including high-pressure pumps, columns, detectors, and sample vials to perform its analysis. Sample vials play an essential role as they contain samples to be analyzed but may leach contaminants that skew results and hinder accuracy – this process known as silanization can treat vials to prevent leaching to improve the accuracy of HPLC analysis.
Importance of Silanized Vials for HPLC Analysis Silanization is a chemical process in which silane compounds react with the surface of vials to form a hydrophobic coating that repels water, thereby preventing contamination of samples through leaching into them. Utilization of silanized vials provides several advantages when used for HPLC analysis:
1. Prevents Sample Contamination.
Silanized vials provide an inert surface that prevents the leaching of contaminants into samples, which could potentially alter HPLC analysis results and produce inaccurate results.
- Enhancing Sample Recovery
Silanized vials improve sample recovery by preventing its adhesion to their surface, leading to more accurate and precise analyses of samples collected within them. - Increase Reproducibility of Results
Siliconized vials ensure consistency and reproducibility in HPLC analysis results, which is especially crucial for high-throughput laboratories that depend on accurate and reliable information for decision-making. - Prevents Ghost Phenomena
Ghost peaks are unwanted extraneous peaks that appear on chromatograms due to contaminants leached from vials, creating unwanted extraneous peaks on your chromatogram. Silanized vials prevent this problem by eliminating ghost peaks forming, leading to cleaner and more accurate chromatograms.
I. Silanization of HPLC Vials
1.Definition of Silanization
Silanization is a chemical process used to modify the surface properties of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) vials, specifically those designed for liquid chromatography analysis. This involves covalently attaching organosilane molecules onto their surfaces through covalent bonding to create a thin layer of silane molecules on them that can enhance various characteristics such as increasing wettability on vial surfaces, decreasing sample components adsorption onto vial walls, and improving stability during analysis. This article will detail these steps further as well as factors influencing successful silanization efforts.
2. Three Steps Involved in Silanization Mes
The initial step of silanization involves cleaning and prepping HPLC vials with suitable solvents before rinsing them with deionized water for final rinse and drying. Next, they are exposed to a solution containing silane molecules; these attach themselves through hydrolysis and condensation reactions as they dry; afterward, they are heated at an appropriate temperature to drive away any unreacted silanes, while simultaneously cross-linking all silane molecules present.
3. Two Factors Affecting Silanization

The success of silanization depends on various factors, including quality and purity of silanes used, cleanliness of vials used, temperature and duration of silanization reaction as well as various other considerations. Ideally, silanes free from impurities should be utilized since any impurities may lead to incomplete reactions or produce unwanted by-products that reduce the performance of vials.
1. Cleanliness of vials is also key to successful silanization since any residue contaminants on their surfaces could impede silane molecules from attaching properly and lead to poor coverage or incomplete reactions. Therefore, it is crucial that vials be cleaned thoroughly using appropriate solvents before being rinsed with deionized water in order to remove any remaining contaminates.
2. The temperature and duration of silanization reactions can significantly impact their success. Higher temperatures and longer reaction times often result in better coverage and stronger attachment of silane molecules to vial surfaces; however, excessively high temperatures or prolonged reaction times may result in degradation or decomposition of silane molecules causing poor coverage or unwanted side reactions.
Silanization is an integral step in the preparation of HPLC vials for analysis, as it involves covalently bonding organosilane molecules to the vial surface to form a thin film of silane molecules that provides numerous benefits. The success of silanization depends on factors like the quality of silanes used, cleanliness of vials, temperature, and duration of the reaction process – following proper steps with high-grade materials can improve accuracy and reliability during HPLC analyses.
II. Three Applications of Silanized HPLC Vials
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an analytical technique widely utilized across numerous industries, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and environmental analysis. HPLC analysis requires precise and accurate measurements that may be affected by sample components adhering to vial surfaces during sample preparation; using silanized HPLC vials can significantly increase accuracy and reliability by reducing sample component adsorption on vial walls – this article will outline various types of HPLC analysis as well as their benefits as well as examples from various industries where silanized HPLC vials can improve accuracy and reliability when performing HPLC analyses on sample preparation vial walls. In this article we will also give an overview of different types of HPLC analyses as well as applications across various industries that use silanized HPLC vials as sample preparation vessels to enhance accuracy and reliability – these will all be provided here as well.
1. Overview of HPLC Analysis
HPLC analysis can be divided into various types, depending on the separation mechanisms used, such as reverse-phase HPLC, normal-phase HPLC, ion-exchange HPLC, size-exclusion HPLC, and chiral HPLC analysis. No matter which separation mechanism is employed for analysis, accuracy, and reliability will always depend upon proper sample preparation – using high-quality vials that minimize sample component adhesion to vial walls for accurate results.
2. How Silanized Vials Enhance Accuracy and Reliability in HPLC Analysis
Silanized HPLC vials can significantly improve accuracy and reliability by limiting sample component adsorption onto vial walls. Silanization involves applying a thin coating of silane molecules on its surface that improves wettability to help limit sample component adhesion; this leads to better peak shape, SNR ratio, and reproducibility for HPLC analysis.
3. Applications across Industries
There are various applications of silanized HPLC vials across various industries. Pharmaceutical firms use silanized vials for the analysis of drug substances and drug products, improving both accuracy and precision during HPLC analysis for better quality assurance and control. Food and beverage firms use them for food additives analysis such as flavors or fragrances by minimizing sample components adhering to vial walls more reliably resulting in more precise analysis results.
Silanized vials can be an invaluable asset in environmental analysis. Used for testing environmental contaminants like pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals, their accuracy and reliability make HPLC analysis much more precise, leading to improved detection and quantification.
Silanized HPLC vials can enhance the accuracy and reliability of HPLC analysis by minimizing sample component absorption onto vial walls. Silanized vials can be utilized by various industries including pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and environmental analysis to increase the quality & reliability of HPLC results resulting in better quality control & assurance in various fields.
III. Four Benefits of Using Silanized Vials
Silanization, the process by which materials are modified by using silanes to modify their surfaces, has become increasingly popular within HPLC applications due to its numerous advantages over non-silanized vials. We will explore some of these benefits here in detail, such as improved sample recovery rates, decreased surface adsorption rates, enhanced stability, and longer shelf lives.
- One of the primary advantages of silanized vials in HPLC is improved sample recovery. Silanization changes the surface of a vial to become hydrophobic, which reduces sample losses due to adsorption. This leads to better recovery of samples and more accurate results; especially crucial when dealing with low concentrations of analytes where even small losses may have a profound impact on the accuracy of results.
- Reduced surface adsorption is another significant advantage of silanized vials when performing HPLC analyses. Creating a thin film of silane molecules on the vial surface reduces sample components from adhering to it, leading to better peak shapes, increased signal-to-noise ratio, and greater reproducibility of HPLC analysis. It’s particularly helpful when dealing with complex samples where multiple analytes may interact and cause unwanted interactions or adsorption onto vial walls.
3. Silanized vials have the added advantage of improving stability and compatibility with various solvents when used for HPLC analysis, particularly when dealing with samples that require aggressive solvents or contain high levels of salts. Their resistance to chemical attack makes them more stable and compatible with multiple solvents, leading to improved reproducibility in HPLC analyses involving samples requiring aggressive solvents or having high salt contents.
4. Silanized vials offer superior shelf life when compared with non-silanized vials due to their increased stability and resistance to chemical attacks from silanization. They can be stored longer without degrading their properties – an especially advantageous feature in laboratories with large volumes of samples or where vials are used less frequently.
Conclusions regarding silanized vials used in HPLC include improved sample recovery, reduced surface adsorption, enhanced stability, and longer shelf life – these benefits make silanized vials an increasingly popular choice in HPLC labs where precision, accuracy, and reproducibility are vitally important. Utilizing silanized vials enables laboratories to increase the quality and reliability of analyses undertaken and ensure better quality assurance within various industries.

IV. The Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Silanized Vials
Considerations when using silanized vials for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis include their cost-effectiveness. We will compare silanized to non-silanized vials when considering cost-effectiveness as well as savings opportunities related to time and resources as well as long-term advantages of silanization for HPLC analyses.
1. A Comparison of Costs Between Silanized Vials and Non-silanized Vials
Silanized vials may cost more than non-silanized ones, though the difference in cost may not be dramatic. Their use can provide significant time and resource savings. For instance, reduced sample adsorption onto vial walls leads to faster recovery rates which decrease repeat analyses as well as reduce consumption of costly reagents and solvents.
Silanized vials may also provide significant cost-cutting potential due to their extended shelf life and resistance to chemical attacks, meaning they can be stored longer without losing their properties and incurring replacement expenses more frequently over time. This means silanized vials could help save you money in the form of reduced replacement needs and savings on purchasing costs over time.
2. Calculation of Potential Savings in Terms of Time and Resources
To accurately evaluate the savings potential associated with using silanized vials for HPLC analysis, it is crucial to take into account their long-term advantages. Such vials have proven more accurate and reliable results which improve quality control and assurance in various industries and thus contribute to increased customer satisfaction while decreasing product recall or reanalysis costs.
3. The Long-term Advantages of Silanized Vials for HPLC Analysis
Silanized vials can also help enhance laboratory efficiency, as their reduced absorption by sample components leads to faster analysis times and reduced downtime due to equipment maintenance – ultimately leading to increased productivity and decreased labor costs over time.
V. The Importance of Proper Silanization to Achieve Optimized Results
Although the benefits of silanized vials are evident, it’s crucial that we emphasize their proper silanization for optimal results. Any mistakes during this process could compromise their functionality and result in inaccurate outcomes.
Proper silanization requires meticulous attention and strict adherence to established protocols. For best results, use high-grade silanes according to their intended procedures – this will ensure that vials are appropriately coated and functional.
As demand for silanized vials increases, research and development in this field continue apace. Future directions of research may include investigating new silane formulations as well as devising innovative silanization methods in order to increase the performance of silanized vials.
The benefits of silanized HPLC vials are undeniable, including improved sample recovery, reduced surface adsorption, enhanced stability, and extended shelf life. However, to achieve optimal results laboratories must prioritize high-quality silanes and adhere to established protocols when silanizing vials for HPLC analysis. With research advancing this field further, still we expect even greater benefits to emerge from using silanized vials in HPLC analyses.
VI. Challenges of Silanization
Silanization is an indispensable process in HPLC vial production, yet it does present some obstacles. We will discuss some of those difficulties here including achieving consistent results, selecting suitable silane reagents, optimizing process parameters as well as offering strategies to overcome such hurdles.
Silanization poses several distinct challenges, with consistency being among them. The process itself can be affected by various variables including vial type and size, temperature/humidity of the environment, and purity/concentration of silane reagents used – any variations can cause inconsistent or unreliable silanization results.
To combat this challenge, laboratories must create and adhere to stringent quality control protocols for silanization. These should include regular monitoring of environmental conditions, careful selection of vial types, and use of high-purity silanes. Consistent documentation of the silanization process can also help identify any areas for improvement or troubleshooting.
Silanization presents many unique challenges. There are various kinds of silane reagents available, each with its own set of properties and applications; selecting the most suitable silane reagent for an HPLC analysis can be tricky for laboratories that deal with diverse samples.
One strategy to overcome this difficulty is consulting experts in silanization or conducting extensive research in order to find the appropriate silane reagents for specific applications. Laboratories may test multiple silane reagents until one provides optimal results for their specific requirements.
Optimizing the process parameters of silanization is another daunting challenge. Process parameters, such as concentration and application method for silane reagents, can greatly affect its effectiveness; finding optimal parameters may take considerable trial and error before reaching their full potential in one application.
To overcome this challenge, laboratories should conduct extensive optimization studies in order to establish optimal process parameters for silanization. This may require changing various factors like silane concentration, incubation time, and curing temperature in order to identify optimal conditions for successful silanization results.
Silanization is an essential element of HPLC analysis, but it does present several challenges that laboratories must overcome to ensure consistent, reliable, and effective silanization results. Strategies such as creating rigorous quality control protocols, selecting suitable silane reagents, and optimizing process parameters may help overcome some of these difficulties and lead to successful silanization results.
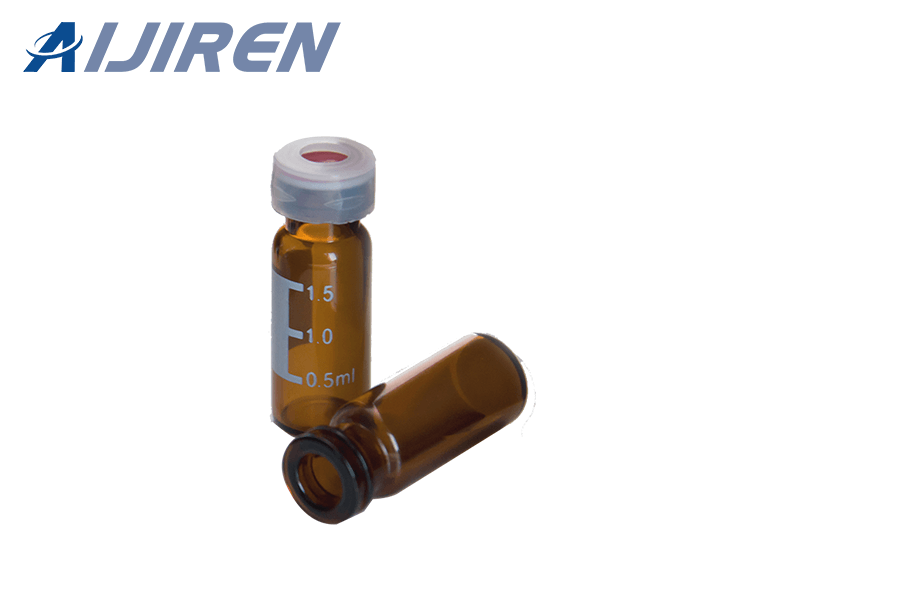

VII. Conclusion
Silanized vials have become an indispensable tool in HPLC analysis. Their silanization process offers numerous advantages, including improved sample recovery, reduced surface adsorption, enhanced stability, and longer shelf life. Silanization also offers cost-effective solutions for laboratories by offering significant time and resource savings.
As we have demonstrated in this article, silanization can present many difficulties. Achieving consistent results while selecting suitable silane reagents and optimizing process parameters may require considerable expertise to successfully implement.
Though silanization presents numerous challenges to HPLC analysis, its potential benefits cannot be overstated. Silanized vials provide more accurate and reliable results making them invaluable tools across industries including pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, environmental analysis, and others.
Silanized vials for HPLC analysis offer numerous advantages that simply cannot be overstated. By addressing any challenges associated with silanization and developing innovative techniques to do it successfully, laboratories can continue to advance HPLC analysis while increasing the accuracy and reliability of results produced from the analysis.
Back to List
-
 下午4:09Weighing the Pros and Cons of PTFE/Silicone Septa
下午4:09Weighing the Pros and Cons of PTFE/Silicone Septa -
 下午4:05Decoding Vial Discard Guidelines: Ensuring Precision in Chromatography
下午4:05Decoding Vial Discard Guidelines: Ensuring Precision in Chromatography -
 下午5:01Navigating Micro Inserts for HPLC Vials: A Comprehensive Guide
下午5:01Navigating Micro Inserts for HPLC Vials: A Comprehensive Guide -
.jpg) 下午2:02Common faults and solutions of automatic samplers(2)
下午2:02Common faults and solutions of automatic samplers(2) -
 下午5:08Ensuring Sample Integrity: Navigating EPA Storage Vials Stability Guidelines
下午5:08Ensuring Sample Integrity: Navigating EPA Storage Vials Stability Guidelines

