A Comprehensive Guide to the Different Types of HPLC Autosampler Vials
I. Introduction
Autosampler vials are small containers that hold samples for automated analysis in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) systems. They play a crucial role in the accuracy and reproducibility of HPLC analysis by making sure that samples are properly stored and delivered to the instrument. In this article, we will explore the different types of autosampler vials, their applications in HPLC analysis, factors to consider when selecting vials, and best practices for using and cleaning them.
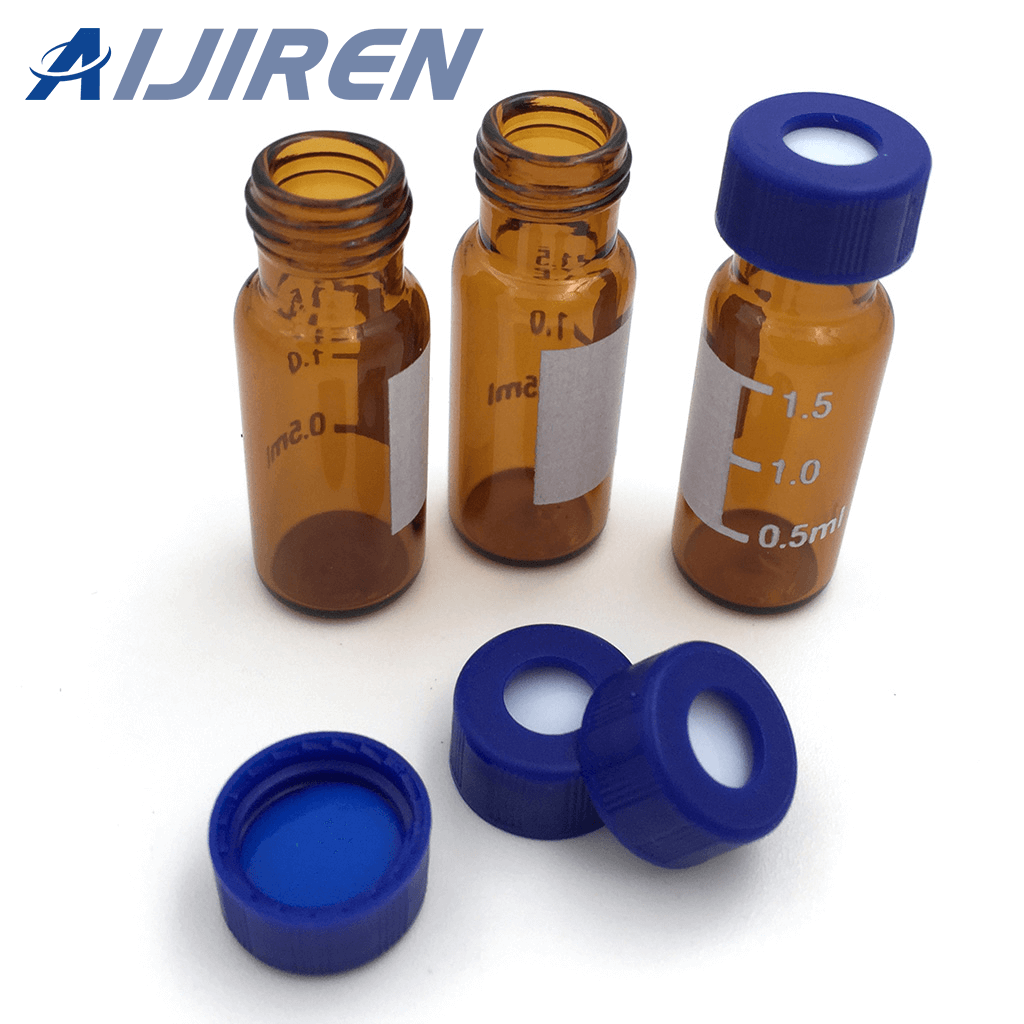

II. HPLC Autosampler Vials
HPLC autosampler vials are used in HPLC analysis. They are made of materials that are compatible with HPLC solvents and can withstand the high pressure and temperature conditions in HPLC systems. There are several types of HPLC autosampler vials, including glass, plastic, and metal. Glass autosampler vials are the most used in HPLC analysis due to their chemical resistance and low extractable content.
III. Applications of Autosampler Vials
Autosampler vials are indispensable in various chemical analysis techniques, such as chromatography and mass spectrometry, where accuracy and precision are of vital importance for analysis results. HPLC autosampler vials can hold and deliver liquid samples for separation and detection in the HPLC system.
IV. What Vials Are Used in HPLC?
The choice of vials is a key point when proceeding with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) analysis. HPLC is an analytical technique that highly requires precision and accuracy to get ideal results. Choosing the right vial is crucial for the sample properly contained, preserved, and delivered to the HPLC instrument.
Importance of vial selection in HPLC analysis
Opting for a suitable vial is pivotal to an HPLC analysis. The vial must be compatible with the sample and the instrument, and it must be capable to stand the stresses of the analysis without compromising the accuracy of the results. Choosing vials can also impact the sensitivity and detection limits of the analysis
V. HPLC vial dimensions
1. Definition of HPLC vial dimensions
HPLC vials come in a variety of shapes and sizes, with different neck styles and thread types. Vial dimensions include diameter, height, and volume. Diameter refers to the widest part of the vial and height refers to the distance from the bottom to the top of the vial. Capacity refers to the amount of liquid a vial can hold. Vial dimensions are usually measured in millimeters (mm)
2. Importance of HPLC vial dimensions in HPLC analysis
HPLC vial dimensions play an important part in HPLC analysis. The vial’s dimensions influence the amount of sample that can be loaded onto the column, the accurate and precise handling of the analysis, and the compatibility with the autosampler. If the vial is too small, it may not hold enough samples for the analysis. On the contrary, if the vial is too large, it may contribute to wasting reagents and rising the cost of the analysis.
3. Common HPLC vial dimensions
Although there are different types of HPLC vials available on the market, with varying dimensions, the most common vial dimensions are as follows:
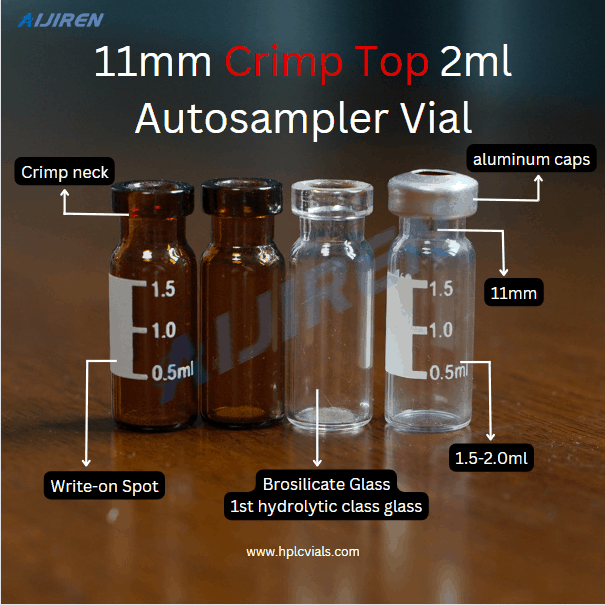
2mL vial dimensions: It is widely used in HPLC analysis, and has a diameter of 12 mm and a height of 32 mm. These vials typically have a neck of 9 mm or 11 mm and a screw thread format.
1.5mL vial dimensions: The diameter of these vials is 11 mm and the height is 32 mm, which makes them slightly smaller than the 2mL vials. They are compatible with most autosamplers and have a neck of 9 mm or 11 mm.
4mL vial dimensions: These vials have a diameter of 15 mm and a height of 45 mm, which makes them larger than the 2 mL vials. They are typically used for samples requiring a larger volume and have a neck of 13 mm.
10mL vial dimensions: The diameter and height of these vials are 23mm and 46 mm. Thus, they are the largest of the commonly used HPLC vials. They are used for samples that require a larger volume and have a neck finish of 20 mm.
4. Factors to consider when selecting HPLC vial dimensions
When choosing HPLC vial dimensions, the type of analysis, the amount of sample available, the compatibility with the autosampler, and the availability of the vial in the ma are consider considered. It is also critical to think about the cost of the vials and their influence on the whole cost of the analysis.
In conclusion, HPLC vial dimensions should be considered in HPLC analysis. The dimensions impact the volume of the sample that can be loaded onto the column, the accuracy and precision of the analysis, and the compatibility with the autosampler. So it is vitally important to take the vial’s dimensions into consideration when choosing a vial for HPLC analysis.
VI. Can You Reuse HPLC Vials?

HPLC Autosampler Vials are an indispensable part of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) analysis. They contain the samples and the standards for HPLC analysis. With the increasingly high cost of research, scientists are always looking for ways to reduce costs. One way is to reuse HPLC Autosampler Vials. But is it safe and efficient to reuse HPLC Autosampler Vials? Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of reusing HPLC vials, factors to consider when reusing them, and best practices.
1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Reusing HPLC Vials
The main advantage of reusing HPLC Autosampler Vials is to save costs. Reusing vials means that they don’t need to purchase constantly. It is obvious that, in the long run, it is expensive. Besides that, reusing vials can be environmentally friendly. However, there are also shortcomings to reusing vials. The risk of contamination is high, which can lead to inaccuracy and unprecision of the results. Contamination can occur from the previous standards that were not completely removed during the cleaning process.
2. Factors to Consider When Reusing HPLC Vials
Before deciding to reuse HPLC Autosampler Vials, consider the following factors. First, the type of analyzed sample. Samples with a high level of contamination are not suited for recycling vials. Second, the sensitivity of the method being used. If the method is highly sensitive, the risk of contamination is great, and it may not be good for recycling. Third, the times vials have been used. The more it is reused, the greater the risk of cross-contamination and impurity.
3. Tips for Reusing HPLC Vials
If you reuse HPLC Autosampler Vials out of certain reasons, remember the following steps. Firstly, clean the vials with a solvent. And then the vials should be dried and checked in case of any contamination. Secondly, make sure that the vials are consistent with the analyzed samples. Lastly, write on the spot of the vials, which can prevent confusion and contamination.
VII. Ways to wash HPLC vials
1. Significance of washing HPLC vials
Cleaning HPLC vials is very helpful for the accuracy and precision of analysis. Contaminated vials can lead to inaccurate results, distorted data, and even instrument failure. HPLC vials can become contaminated with residues from previous samples such as salts, buffers, and solvents, which can interfere with the analysis of subsequent samples. However, if the vials are not cleaned properly, they can be covered with particles and can cause HPLC column failure, leading to inaccurate and unreliable results.
2. Considerations when cleaning HPLC vials
Before cleaning HPLC vials, several factors are necessary to consider:
Contamination type: The type of contamination determines the cleaning method used. For example, if a vial is impure with non-volatile residues, a solvent rinse may not be sufficient and a more aggressive cleaning method may be required.
Solvent Rinsing: The wash solvent used must be compatible with the sample and the HPLC system. It is imperative to avoid solvents that can damage the autosampler seals, plastic, or metal parts.
Time: Overwashing can lead to the introduction of unwanted impurities, and underwashing can lead to inaccurate results, so the time it takes to wash the vials is critical.
Vial material: Vial material can also affect the cleaning process. Glass vials are easier to clean compared to plastic vials or metal vials which may require more aggressive cleaning methods.
3. Methods of Cleaning HPLC Vials
There are several ways to clean HPLC vials, including:
Solvent rinse: This is the easiest and most commonly used method of cleaning HPLC vials. Vials should be rinsed with a proper solvent such as methanol or acetonitrile and dried before use.
Ultrasonic Cleaning: Ultrasonic cleaning uses high-frequency sound waves to agitate the cleaning solution and remove contaminants from the vials. This method works for removing stubborn residues, but you should try to avoid damaging the vial.
Soxhlet Extraction: Soxhlet extraction is a more aggressive cleaning method that involves putting the vial into a solvent and then heating the vial to the boiling point. This method is effective for removing non-volatile residues but can damage the vial and should be used with caution.
Detergent washing: Detergent washing is a mild cleaning method that uses detergents such as Triton X-100 and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) to clean contaminants from vials.
Cleaning HPLC vials is the direct-acting factor of the accuracy and precision of the analysis. Contaminated vials can lead to inaccurate results, skewed data, and even do harm to the instrument.
Ⅷ. HPLC Autosampler Vial Price

HPLC autosampler vials are a critical part of chromatographic analyses, but these vials cost a lot. This part explores the factors that affect the price of HPLC autosampler vials, compares different types of vials, and provides tips for choosing affordable vials.
1. Factors affecting the price of HPLC autosampler vials
There are factors that can impact the price of HPLC autosampler vials. One of the most important factors is the material the vials are made from. Generally speaking, glass vials are more expensive than plastic vials, and certain types of glass, such as borosilicate glass, are more expensive than others.
Size and shape can also affect the price. Large vials are generally more expensive than smaller vials, and vials with unique shapes and features also can be more costly.
Other factors that can affect the price of HPLC autosampler vials cover the manufacturing process, cap or closure type and quality, and supplier or brand.
2. Comparison of Different HPLC autosampler vials
There are several types of HPLC autosampler vials on the market, and each has its own strengths and shortcomings. Glass vials are the most used vials and hold a variety of sizes and shapes. Borosilicate glass vials are particularly popular due to their resistance to high heat and low extractable content.
Plastic vials are a cheaper option and are often preferred when breakage is a concern. However, plastic vials are not a better choice when it comes to resisting high temperatures than glass vials and may not be compatible with certain solvents.
3. Tips for choosing affordable HPLC autosampler vials
1). Consider your specific needs: Consider your analytical requirements and choose a vial that meets those needs without rising up costs.
2). Shop around: Compare prices from all kinds of suppliers and brands to find the best one.
3). Consider buying in bulk: Many suppliers offer discounts when you want to purchase in bulk.
4). Consider alternative materials: Plastic vials are a more affordable option, but make sure they are compatible with your analysis.
5). Choose Simpler Closures: Vials with complex or specialized closures can be more expensive than vials with standard closures.
In conclusion, the price of HPLC autosampler vials depends on several factors. Glass vials are the most common and widely used type of vials, but plastic and metal vials can be more affordable according to your specific needs.
HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) analysis is a widely used technique for separating, identifying, and quantifying chemical constituents in samples. Using high-quality autosampler vials is critical for accurate and reliable results.
Autosampler vials play an important part in HPLC analysis as they contain the samples that are injected into the instrument for analysis. High-quality materials must be used to make these vials and they should be free from impurities and contaminants that could affect results. Additionally, it must be compatible with the instrument, sample volume, and type of analysis. Factors such as material, size, and price should be considered when selecting vials and best practices should be followed when reusing. By considering these factors, researchers can ensure that HPLC analytical results are accurate and reliable.
Back to List
-
 下午4:09Weighing the Pros and Cons of PTFE/Silicone Septa
下午4:09Weighing the Pros and Cons of PTFE/Silicone Septa -
 下午4:05Decoding Vial Discard Guidelines: Ensuring Precision in Chromatography
下午4:05Decoding Vial Discard Guidelines: Ensuring Precision in Chromatography -
 下午5:01Navigating Micro Inserts for HPLC Vials: A Comprehensive Guide
下午5:01Navigating Micro Inserts for HPLC Vials: A Comprehensive Guide -
.jpg) 下午2:02Common faults and solutions of automatic samplers(2)
下午2:02Common faults and solutions of automatic samplers(2) -
 下午5:08Ensuring Sample Integrity: Navigating EPA Storage Vials Stability Guidelines
下午5:08Ensuring Sample Integrity: Navigating EPA Storage Vials Stability Guidelines

